MCAT Biology Practice Questions
/Master MCAT Biology using focused practice problems, essential topic breakdowns, and proven techniques to improve accuracy and retention.
(Note: This resource also appears in our MCAT Ultimate Guide.)
----
Introduction
MCAT Biology Practice Passage #1
MCAT Biology Practice Passage #2
MCAT Biology Practice Passage #3
MCAT Biology Practice Questions (Standalone)
----
Introduction
You’ve taken all of your premed classes and are ready to start prepping for the MCAT. You already made a great study schedule, have started content review, and are ready to start taking some more practice problems.
Unlike most tests you’ve taken before in undergrad, the MCAT is an entirely different challenge. The exam is difficult and long, especially if you don’t prepare the right way. As you progress further in your medical training, your method of studying will shift from content review to practice problems. The MCAT is no exception—practice problems will help to significantly improve your score.
Don’t worry, though. We have you covered. Biology is an important subject on the MCAT, and you’ll see biology in the chemistry/physics, biology/biochemistry, and psychology/sociology sections of the exam. Therefore, you’ll need to be ready to answer bio questions asked in a variety of contexts.
Here, we’ll test your biology knowledge using MCAT-style passages written by a 528 scorer. The MCAT relies heavily on repurposing scientific articles and then asking you questions about those articles. As a result, you need to be able to sift through scientific data and answer questions that combine information from the passage with your outside knowledge.
Use the following three biology passages and five standalone questions to test your ability to apply your biology knowledge to real, MCAT-style passages. Each explanation for the passage-based questions will have suggestions for what you should review if you miss a question. Good luck!
----
MCAT Biology Practice Passage #1
Postoperative acute kidney injury (AKI) is a severe complication after liver transplantation (LT) as its deterioration and magnification can lead to an increase in mortality. Connexin43 (Cx43) mediates direct transmission of intracellular signals between neighboring cells, always considered to be the potent biological basis of organ damage deterioration and magnification.
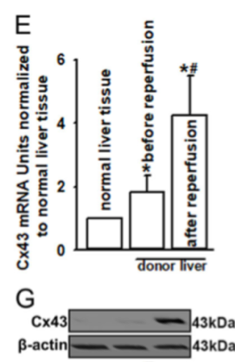
Researchers obtained donor liver tissues of patients in order to explore the effects of Cx43 on organ damage. Reperfusion is a biological process used to refill blood in AKI. Donor livers displayed more severe lobular distortion with necrosis, apparent edema, hemorrhage, and neutrophil infiltration after reperfusion, compared with donor liver tissues obtained before reperfusion or normal liver tissue (from patients with hepatic hemangioma). After reperfusion, Cx43 mRNA and protein levels were determined as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Cx43 mRNA and protein levels in normal or donor livers, before reperfusion, and after reperfusion.
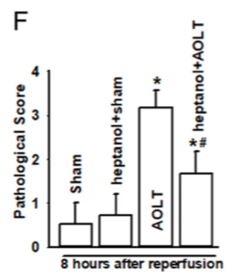
Autologous orthotopic liver transplantation (AOLT) rats were built by researchers in order to further study AKI. Researchers hypothesized that the change in Cx43 expression might play an important role in AKI following AOLT. Researchers used heptanol, a well-known inhibitor of Cx43 without hepatotoxicity, to alter the function of junctions composed of Cx43. Heptanol had no effects on Cx43 expression in kidneys or livers.
Heptanol or a sham control were injected intravenously into the rats, and the pathological score of kidney cells was determined to analyze disease progression. The results are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Pathological score of AOLT mice treated with Cx43 inhibitor.
Researchers also believe that the RIP1 may be involved in Cx43 function, and they confirmed the interaction of the proteins through co-immunoprecipitation. RIP1 is a typical marker of necroptosis.
1. What type of junction does Cx43 most likely form?
A) Gap junction
B) Tight junction
C) Desmosome
D) Hemidesmosome
2. A researcher discovers a new Cx43 inhibitor made of a glycerol backbone and three saturated fatty acid tails. Which of the following describes the path by which the inhibitor enters the cells?
A) The inhibitor is recognized by a specific receptor.
B) The inhibitor is taken up by a non-specific receptor.
C) The inhibitor diffuses through the cell membrane.
D) The inhibitor passes through the cell membrane via a channel.
3. Researchers decide to interrupt the Cx43-RIP1 interaction in the AOLT rat model without using a small molecule inhibitor. Which of the following will most likely disrupt the interaction?
A) SiRNA for RIP1
B) Radiation against heptanol
C) Acetyltransferase specific for β-actin
D) Plasmid producing Cx43
4. Which conclusion about Cx43 regulation is best supported by Figure 1?
A) All expression control occurs at the transcriptional level.
B) All expression control occurs at the translational level.
C) Donor livers have higher levels of Cx43 after reperfusion when compared to normal liver tissue.
D) Normal livers treated with heptanol have lower levels of Cx43 compared to donor livers treated with heptanol.
Answer key for practice passage #1
1. Answer choice A is correct. Cx43 is a connexin protein as stated by the passage, and connexins form gap junctions (choice A is correct).
Review junction types.
2. Answer choice C is correct. The inhibitor described in the question stem is very hydrophobic, and this means it will pass through the membrane via diffusion (choice C is correct).
Review plasma membrane composition and properties.
3. Answer choice A is correct. SiRNAs bind to mRNAs for certain genes and lead to degradation. If the RIP1 mRNA is degraded, Cx43 will no longer be able to interact with RIP1 (choice A is correct). Radiation is highly non-specific and would likely affect other processes (choice B is incorrect). β-actin is not involved in the Cx43-RIP1 interaction based on information from the passage (choice C is incorrect). A plasmid producing Cx43 would likely not be taken up by the rat cells, and an increase in Cx43 expression should not disrupt the interaction (choice D is incorrect).
Review siRNAs.
4. Answer choice C is correct. The graph in Figure 1 shows that donor livers have higher expression levels of Cx43 mRNA when compared to normal liver tissue (choice C is correct). The mRNA expression levels given by the graph and the protein expression levels given by the blot are different, meaning that regulation occurs at both the transcriptional and translational levels (choices A and B are incorrect). Heptanol is not addressed in Figure 1 (choice D is incorrect).
Review transcription versus translation. Practice interpreting experimental data, and make sure to understand the figure completely.
Gain instant access to the most digestible and comprehensive MCAT content resources available. 60+ guides covering every content area. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.