RNA for the MCAT: Everything You Need to Know
Learn high-yield RNA topics for the MCAT, including mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, gene expression, and common traps, plus practice questions.
(Note: This guide is part of our MCAT Biochemistry series.)
Part 1: Introduction to RNA
Part 2: Structure of RNA
a) Similarities to DNA
b) Differences with DNA
Part 3: Functions of RNA
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) snRNA
Part 4: High-yield terms
Part 5: Passage-based questions and answers
Part 6: Standalone questions and answers
----
Part 1: Introduction to RNA
What is RNA?
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is one of the two types of nucleic acids. You may know the other as DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is important because it stores, selectively expresses, and transmits the genetic information our cells need to function. Although RNA serves a different purpose in the cell, it’s just as important as DNA!
RNA plays a vital role in proper genetic expression, helping create proteins that can enact changes in the cell. Outside of genetic expression, RNA can have catalytic functions throughout the cell, similar to enzymes. In fact, the abundance of non-coding RNA with catalytic function and RNA’s similarity to DNA supports the “RNA world,” suggesting that before DNA, RNA was the basis of life. Given how powerful RNA can be, understanding the different functions of RNA is necessary on the MCAT.
When studying RNA, it’s easy to confuse RNA and DNA because of their similarities. Both nucleic acids use similar coding languages and are involved in genetic expression. RNA also has a host of other functions outside of its involvement with the genetic code. As you read through this guide, organizing the differences between RNA and DNA as well as the different types of RNAs and their functions in a table can be useful. We’ve included an example later in this guide. Feel free to build upon it as you learn more about RNA!
Let’s get started!
----
Part 2: Structure of RNA
a) Similarities to DNA
Since RNA and DNA share similar structures, we can start by comparing the two structures. Core to both RNA and DNA is their nucleic acid structure. This means that both molecules are composed of nucleotides and are chained together by a sugar phosphate backbone. This nucleic acid structure is shown below.
Figure: Nucleic acid structure of DNA (left) and RNA (right).
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. Combinations of nucleotides store the genetic information in RNA and DNA, and replication of these combinations makes inheritance possible. Each nucleotide consists of three different groups bound together: a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base on each nucleotide is slightly different, giving each nucleotide a unique identity. In DNA, the four nucleotides are known as adenosine monophosphate (adenine), guanosine monophosphate (guanine), cytidine monophosphate (cytosine), and deoxythymidine monophosphate (thymine).
RNA uses three of the same nucleotides: adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Instead of deoxythymidine monophosphate, RNA uses uridine monophosphate (uracil). We’ve highlighted the overlap and differences in nucleotide use between DNA and RNA in the Venn diagram below.
Figure: Nucleotides used in DNA and RNA.
b) Differences with DNA
When comparing the structures of RNA and DNA, it is important to note some key differences. One of the most striking differences is the double-stranded versus single-stranded status of the nucleic acids. DNA is double-stranded while RNA is single-stranded.
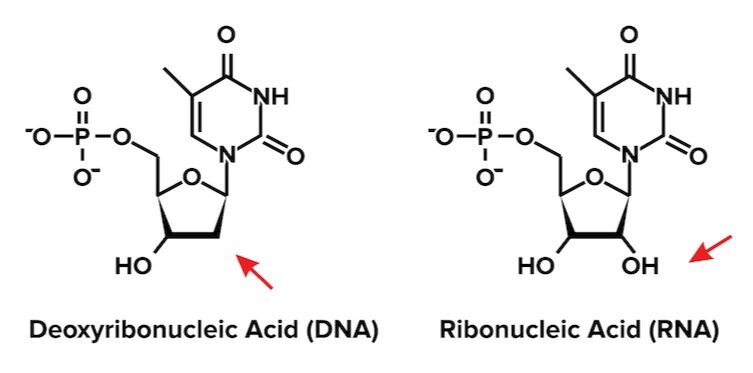
Figure: Organic structure of DNA (left) and RNA (right).
To understand why DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded, let’s think about their functions in the cell. DNA is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information between generations. It is advantageous for the cell to minimize the damage and degradation DNA suffers. As a result, DNA needs to be stable. A double-stranded motif provides DNA the stability it needs.
On the other hand, RNA is produced when a protein is needed and degraded afterward. Its use is temporary. As a result, RNA does not need to be as stable as DNA. In fact, RNA must be degraded. A single-stranded structure allows RNA to pass genetic information and be quickly recycled once it has completed its function.
Another important but subtle structural difference between RNA and DNA lies in their nucleotides. Recall that nucleotides have three distinct groups: a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base provides each nucleotide with a unique identity.
Now, let’s turn our attention to the pentose sugar or ribose. The ribose sugar in RNA is slightly different from the sugar found in DNA. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. The prefix ribo tells us that RNA contains a normal ribose sugar. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. The prefix deoxyribo tells us that the ribose sugar in DNA lacks a hydroxyl group at the 2’ position. Knowing this trick is a handy way to remember the differences in structure between RNA and DNA. We’ve illustrated the difference between the ribose sugars in DNA and RNA below.
Gain instant access to the most digestible and comprehensive MCAT content resources available. 60+ guides covering every content area. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.
Figure: Deoxyribose in DNA (left) lacks a hydroxyl group at the 2’ position.
| DNA | RNA |
|---|---|
Figure: Similarities and differences between DNA and RNA
----
Part 3: Functions of RNA
a) mRNA
The central dogma of biology states that DNA must be transcribed to create RNA. Transcription is a complex molecular process resulting in the translation of genetic information from DNA’s nucleotides to RNA nucleotides. An enzyme known as RNA polymerase serves as a translator to synthesize an RNA transcript. RNA polymerase knows where to start and stop translating based on cues provided in the DNA. Just as we know to start and stop reading a sentence from the capitalized letter at the beginning and period in the end, RNA polymerase is given similar cues. In addition to recognizing specific start and stop points for translation, RNA polymerase creates a transcript where each thymine read in the original DNA is replaced with uracil in the resulting RNA.
Once an RNA transcript is synthesized, it must undergo modifications before its final version is ready for translation. Imagine having a 10-page research paper due at the end of the term. At the beginning of the writing process, you may start with a lengthy rough draft. As you move through the editing process, you may remove and add new information until the final version is ready to be submitted.
RNA transcripts go through a similar revision process, known as posttranscriptional processing. One type of posttranscriptional processing is splicing. RNA transcripts are composed of two types of segments, called introns and exons. Introns are RNA sequences that do not encode information for protein translation. Exons are RNA sequences that do encode information for protein translation. A special enzyme, known as a spliceosome, is responsible for splicing: removing introns and ligating exons from RNA transcripts. Additional enzymes add a 5’ cap and poly-A tail, which stabilize the transcript and protect it from degradation in the cytosol. At the end of this complex process, the RNA transcript is considered mature and is ready to serve its job as mRNA, or messenger RNA.
Not all exons are always required in an RNA transcript. A single RNA transcript can be spliced in various ways: differing combinations of exons can be kept or discarded. This phenomenon is known as alternative splicing. Because of alternative splicing, one gene can give rise to multiple proteins.
b) tRNA
The second half of the central dogma states that RNA creates protein. How does this happen?
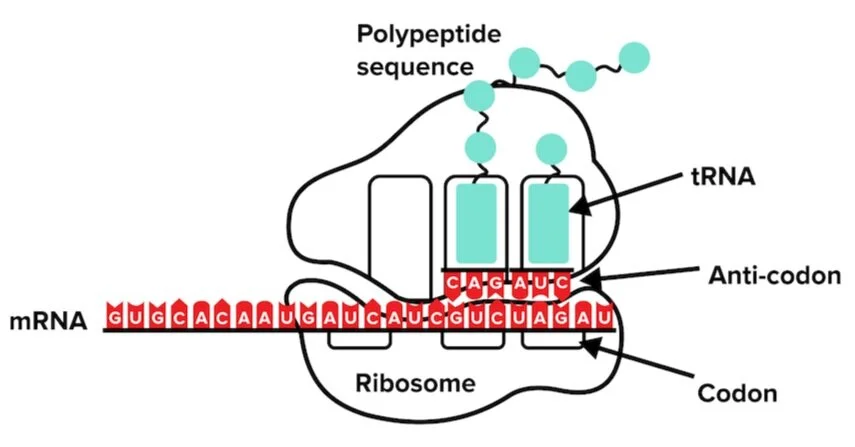
RNA creates protein in a process known as translation. Translation occurs in the ribosomes, which are also made of RNA. (More on ribosomal RNA later.) In this process, ribosomes bind and read codons in mRNA transcripts. Codons are sequences of three nucleotides. Each codon will translate a specific amino acid. For example, the nucleotide sequence AUG represents a codon. The AUG codon specifies the amino acid methionine, which will be used to start a growing chain of peptides. The codon AUG indicates the start of the polypeptide sequence while codons UAA, UAG, UGA signal the ribosome to stop translation. It is useful to know these start and stop codons, as they may appear on the MCAT. You may also be provided with a translation table, which will depict how to translate codons into amino acids.
The ribosome may be able to read the codons, but how are amino acids added? The answer lies in another type of RNA known as transfer RNA, or tRNA. tRNAs (shown below) contain two crucial components that help translation function. Each tRNA contains a unique anticodon loop and an amino acid it is charged with. tRNA anticodons are able to bind to complementary mRNA codons. Once bound, the tRNA can transfer its amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. Recall that the start codon AUG encodes the amino acid methionine. This codon is matched by a tRNA with the complementary anticodon UAC. The same tRNA molecule, which carries a methionine molecule with it, will transfer the amino acid to the polypeptide sequence formed in the ribosome.
Figure: An overview of protein translation.
Initiation factors are proteins that assist in beginning translation. These factors direct the binding of a ribosome to an RNA transcript and also in bringing a tRNA molecule closer to the protein elongation site. When a stop codon is encountered and translation is completed, termination factors then assist in the release of the RNA transcript from the ribosome.
You may note that there are more combinations of codons than are possible than there are amino acids. While there are 43, or 64 codons that can be formed by nucleotides, there are only 21 translated amino acids. As a result, multiple codons may code for the same amino acid. This is a phenomenon known as degeneracy.
For example, the amino acid alanine can be encoded by multiple codons: including GCU, GCA, GCC, GCG. You may note that while these four codons all share identical nucleotides in the first two positions, the third nucleotide does not seem to be as important. This is made possible by the wobble effect, or non-Watson Crick base pairing that allows for weak binding between the third nucleotide of the codon in mRNA and anticodon in tRNA. Thus, multiple codons can translate to the same amino acid—without requiring the presence of 64 unique tRNA molecules!
c) rRNA
RNA in the cell is not only present as mRNA and tRNA, but also as ribosomal RNA and snRNPs. Ribosomal RNA and snRNPs are two types of RNA that have catalytic properties.
Ribosomal RNA, or rRNA, is the main component of ribosomes. rRNA combines with special proteins to create the small and large subunits of the ribosome. These two subunits of the ribosome perform the act of translation.
It is important to remember that RNA has functions beyond that of simply encoding genetic information. RNA can also function as a helper molecule in different reactions, such as the translation of genetic information into proteins.
RNA molecules that are able to perform chemical reactions independently are referred to as ribozymes, or “ribosomal enzymes.” Ribozymes can function as catalysts in reactions and behave very similarly to some protein enzymes, despite the fact that they are composed solely of RNA!
The sizes of the strands of rRNA in each subunit are measured in Svedbergs, denoted by a capital “S.” In eukaryotes, the small subunit of ribosomes (also known as the 40S subunit) contains 18S rRNA, while the large subunit (also known as the 60S subunit) contains 28S rRNA. In prokaryotes, the subunits and rRNA are slightly smaller. The small subunit, or 30S subunit, consists of a 16S rRNA, while the large subunit, or 50S subunit, contains a 23S rRNA. Together, eukaryotic ribosomes have a size of 80S while prokaryotic ribosomes have a size of 70S.
Learning the sizes of the ribosome’s subunits and associated rRNA can initially be quite confusing. A handy mnemonic to memorize subunit size for prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes is to use the multiples of 10 from 30 to 80. Every other multiple of 10 is grouped together, with the smaller two multiples representing the sizes of the small and large subunits in each group. The two groupings look like this: 30 (small subunit), 50 (large subunit), 70 (ribosome size) and 40 (small subunit), 60 (large subunit), 80 (ribosome size). Additionally, it may be useful to remember that eukaryotic ribosomes are slightly larger.
Try coming up with your own mnemonic devices to memorize rRNA subunit sizes!
d) snRNA
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, or snRNPs, are complexes of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and proteins. snRNAs are exactly what they sound like: small fragments of RNA. snRNPs combine with pre-mRNA to form a spliceosome.
Recall that the spliceosome is responsible for RNA processing to create mRNA. snRNPs play a vital role in recognizing introns and exons. The complex of RNA and proteins in snRNPs help create specificity for certain sequences that are to be cut.
An important note about RNA is that a variety of RNA and RNA functions exist in the cell. The types and functions of RNA we discussed—including mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and snRNPs—account for most of the content you will be expected to learn for the MCAT, but do not comprise all possible RNA functions.
| RNA type | Function |
|---|---|
Figure: An overview of various types of RNA and their functions.
Out of the four types of RNA that we have discussed, note that only mRNA is translated into a protein product. While mRNA is considered to be coding RNA, the other three types of RNA are considered to be types of noncoding RNA. Noncoding RNA refers to any type of RNA that is transcribed from DNA but is not destined for translation into a final protein product.
----
Part 4: High-yield terms
Ribonucleic acid (RNA): a form of nucleic acid that typically exists in single-stranded form; contains ribose in its phosphate backbone
Nucleic acid: molecules composed of nucleotides, chained together by a sugar phosphate backbone
Nucleotides: the basic building blocks of nucleic acids; includes adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Uracil: uridine monophosphate; a nucleotide taking the place of thymine in RNA
Transcription: the first step of the Central Dogma; results in the transcription of genetic information from DNA’s nucleotides to RNA nucleotides
RNA polymerase: an enzyme that serves as a translator to synthesize an RNA transcript
Splicing: a form of posttranscriptional processing in which introns are removed and exons are ligated together
mRNA: messenger RNA; carries information from the nuclear DNA to ribosomes for translation
Alternative splicing: a phenomenon in which one gene can give rise to multiple proteins by retaining different combinations of RNA exons
Translation: the second step of the Central Dogma; occurs in ribosomes and results in the translation of RNA nucleotides into polypeptides
Codons: sequences of three nucleotides; complementary to anticodons
tRNA: transfer RNA; each tRNA contains a unique anticodon loop and an amino acid it is charged with
Degeneracy: a phenomenon that results in multiple nucleotide codons encoding the same amino acid
Wobble effect: non-Watson Crick base pairing that allows for weak binding between the third nucleotide of the codon in mRNA and anticodon in tRNA
rRNA: ribosomal RNA; main component of ribosomes; combines with special proteins to create the small and large subunits of the ribosome
snRNPs: small nuclear ribonucleoproteins; complexes of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and proteins that combine with pre-mRNA to form a spliceosome
----
Part 5: Passage-based questions and answers
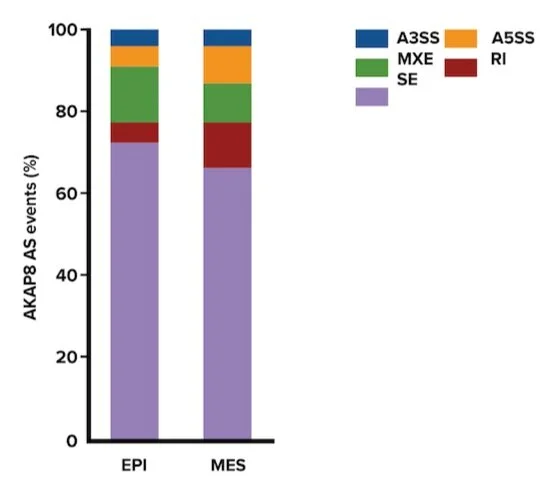
AKAP8 was recently reported as an RNA-binding protein capable of binding to mRNA and regulating alternative splicing. Given observations that AKAP8 interacts with hnRNPM (a splicing factor) and regulates CD44 minigene splicing, scientists sought to interrogate whether AKAP8 regulates global alternative splicing, especially in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Scientists identified AKAP8-regulated splicing alterations totaling 144 and 228 alternative splicing events in epithelial and mesenchymal states, respectively. Figure 1 depicts all observed splicing events.
Figure 1: Splicing events regulated by AKAP8.
CREATOR AND ATTRIBUTION PARTY: HU, X., HARVEY, S.E., ZHENG, R. ET AL. THE RNA-BINDING PROTEIN AKAP8 SUPPRESSES TUMOR METASTASIS BY ANTAGONIZING EMT-ASSOCIATED ALTERNATIVE SPLICING. NAT COMMUN 11, 486 (2020). THE ARTICLE’S FULL TEXT IS AVAILABLE HERE: HTTPS://WWW.NATURE.COM/ARTICLES/S41467-020-14304-1. THE ARTICLE IS NOT COPYRIGHTED BY SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING. DISCLAIMER: SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING DOES NOT OWN THE PASSAGE PRESENTED HERE. CREATIVE COMMON LICENSE: HTTP://CREATIVECOMMONS.ORG/LICENSES/BY/4.0/. CHANGES WERE MADE TO ORIGINAL ARTICLE TO CREATE AN MCAT-STYLE PASSAGE.
Question 1: AKAP8 is likely part of which of the following complexes?
A) Spliceosome
B) DNA polymerase
C) RNA polymerase
D) tRNA
Question 2: What is one way scientists could limit the number of AKAP8 proteins in the cell?
A) Introduce a protein that limits the replication of DNA
B) Introduce a protein that limits the transcription of DNA
C) Introduce a protein that limits the replication of RNA
D) Introduce a protein that limits the translation of DNA
Question 3: How many categories of alternative splicing does AKAP8 regulate?
A) 8
B) 144
C) 5
D) 228
Question 4: Scientists want to know where exactly in the cell AKAP8 is located. To find out, they attach a fluorescent marker to AKAP8. Given AKAP8’s functions, where would the scientists expect AKAP8 to localize?
A) Ribosome
B) Endoplasmic reticulum
C) Golgi apparatus
D) Nucleus
Answer key for passage-based questions
1. Answer choice A is correct. The passage says that AKAP8 regulates alternative splicing and interacts with a hnRNPM, a splicing factor. Together, these clues indicate that AKAP is involved with spliceosome activity (choice A is correct). DNA polymerase is involved in DNA replication (choice B is incorrect). RNA polymerase is involved in transcription (choice C is incorrect). tRNA is involved in protein translation (choice D is incorrect).
2. Answer choice B is correct. Limiting the number of proteins in a cell can be done in multiple ways. One of the best ways to limit the number of proteins would be to block transcription of the RNA that encodes the protein (choice B is correct). Blocking replication would inhibit DNA replication, while failing to limit AKAP8 (choice A is incorrect). Replication refers to the reproduction of DNA (choice C is incorrect), while translation refers to the production of proteins from mRNA (choice D is incorrect).
3. Answer choice C is correct. From the information provided in Figure 1, there are five possible outcomes of splicing that are illustrated in the table (choice C is correct). AKAP8 regulates 144 and 228 individual events in epithelial and mesenchymal states (choices B and C are incorrect).
4. Answer choice D is correct. Based on the passage, we know that AKAP8 is involved with alternative splicing of RNA transcripts. RNA transcripts are processed in the nucleus. Thus, we would expect to find AKAP8 in the nucleus (choice D is correct). Splicing does not occur in the ribosome (choice A is incorrect). The Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum are involved in protein packaging and transport, respectively (choices B and C are incorrect).
Want more MCAT Practice Questions? Check out our proprietary MCAT Question Bank for 4000+ sample questions and eight practice tests covering every MCAT category.
Gain instant access to 4,000+ representative MCAT questions across all four sections to identify your weaknesses, bolster your strengths, and maximize your score. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.
----
Part 6: Standalone practice questions and answers
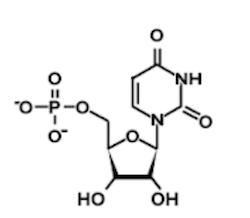
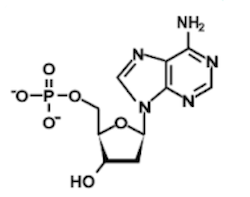
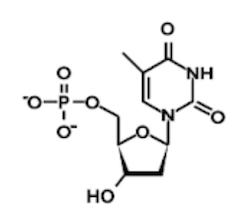
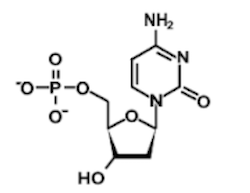
Question 1: Which of the following structures contains an uracil base?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Question 2: What polypeptide sequence would result from translation of the following mRNA sequence?
5’AUGUAUAACCAUCACUAAAUGCCCAAA3’
A) Met, Tyr, Asn, His, His, Stop, Met, Pro, Lys
B) Met, Tyr, Asn, His, His, Stop
C) Met, Trp, Arg, His, His, Stop, Met, Pro, Lys
D) Lys, Pro, Met, Stop, His, His, Asn, Tyr, Met
Question 3: A gene encodes a protein 400 amino acids long. Before RNA processing, there was an intron of 6 base pairs interspersed between every 100 base pairs. How many base pairs was the original RNA transcript before processing?
A) 1269
B) 424
C) 1200
D) 1272
Question 4: Which of the following prevents proper protein translation?
I. Defective RNA polymerase
II. Mutated stop codons
III. tRNAs lacking anticodons
A) I
B) I, II, and III
C) II and III
D) III
Answer key for standalone questions
1. Answer choice A is correct. The other nucleotide structures depicted are adenine, thymine, and cytosine, respectively (choices B, C, and D are incorrect).
2. Answer choice B is correct. Recall that the codon AUG will be translated to methionine. This nucleotide sequence will be translated in the 5’ to 3’ direction (choices C and D are incorrect). The ribosome will stop translating the nucleotide sequence as soon as it encounters a stop codon, such as UAA (choices A and C are incorrect).
3. Answer choice A is correct. Working backward, we see that the 400 translated amino acids must be encoded by at least 1200 nucleotides (choice B is incorrect). In addition, every 100 base pairs had a 6 base pair intron that was excised. In a 1200 base pair sequence, this means that there were 11 introns and thus 66 base pairs of introns excised. Added together, the original RNA transcript contained at least 1266 base pairs (choice C is incorrect). Finally, the mRNA transcript must contain a final stop codon that is not translated into an amino acid. As a result, there must be 1269 base pairs in the original transcript (choice A is correct).
4. Answer choice C is correct. Proper protein translation by a ribosome requires the ribosome to be able to recognize start and stop signals on mRNA (II), as well as having tRNAs ready to transfer amino acids (III). If either component is defective, the ribosome will not be able to properly translate proteins (choice C is correct). RNA polymerase is not involved in protein translation (I).