MCAT Biochemistry Practice Questions
Prepare for MCAT Biochemistry with high-yield practice questions, key concept reviews, and expert strategies to boost your understanding and score.
try solving curated mcat biochemistry practice questions
----
Introduction
You are ready to sit down and study for the MCAT, which is one of the most important pieces of your medical school application. Achieving a great MCAT score can greatly increase your chances of hearing “We’re pleased to inform you…” from the medical school of your dreams.
Your test date looms in the future, and you’re in the thick of your test preparation. You’ve created a perfect study schedule and have started diving into your content review. But, you find that content review is not enough to score well on the MCAT! You need to be able to apply your content knowledge to the rest of the exam.
Biochemistry is one of the most heavily tested subjects on the MCAT. From enzymes to experimental techniques (link experimental techniques page), biochemistry questions will make up a portion of both your chemistry/physics and biology/biochemistry section scores.
Use the following three passages and five standalone questions to test your ability to apply your biochemistry knowledge to real, MCAT-style passages. You’ll notice that each explanation has suggestions for what you should review if you miss a question. Let’s get started, and good luck!
----
MCAT Biochemistry Practice Passage #1
Nuclear estrogen receptor 2 (ERB2) suppresses tumor growth and modulates cancer cell proliferation in breast cancer (BC). Loss of ERB2 is shown to correlate with early stages of ductal and breast tumors, though the specific mechanism is largely unknown. Researchers hypothesized that identifying and characterizing multiprotein complexes involved in ERB2 function might identify the molecular basis for the role of protein in BC.
Using interaction proteomics, which combines native protein complex purification and mass spectroscopy, it was determined that ERB2 interacts with other proteins in BC cells, and this interaction is mediated by one or more RNAs.
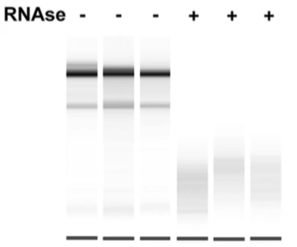
To probe the effect of RNA on ERB2 complex formation, researchers treated a nuclear extract containing ERB2 and its putative binding partners with RNase. The results from the experiment are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Western blot analysis of ERB2 migration without or without RNase.
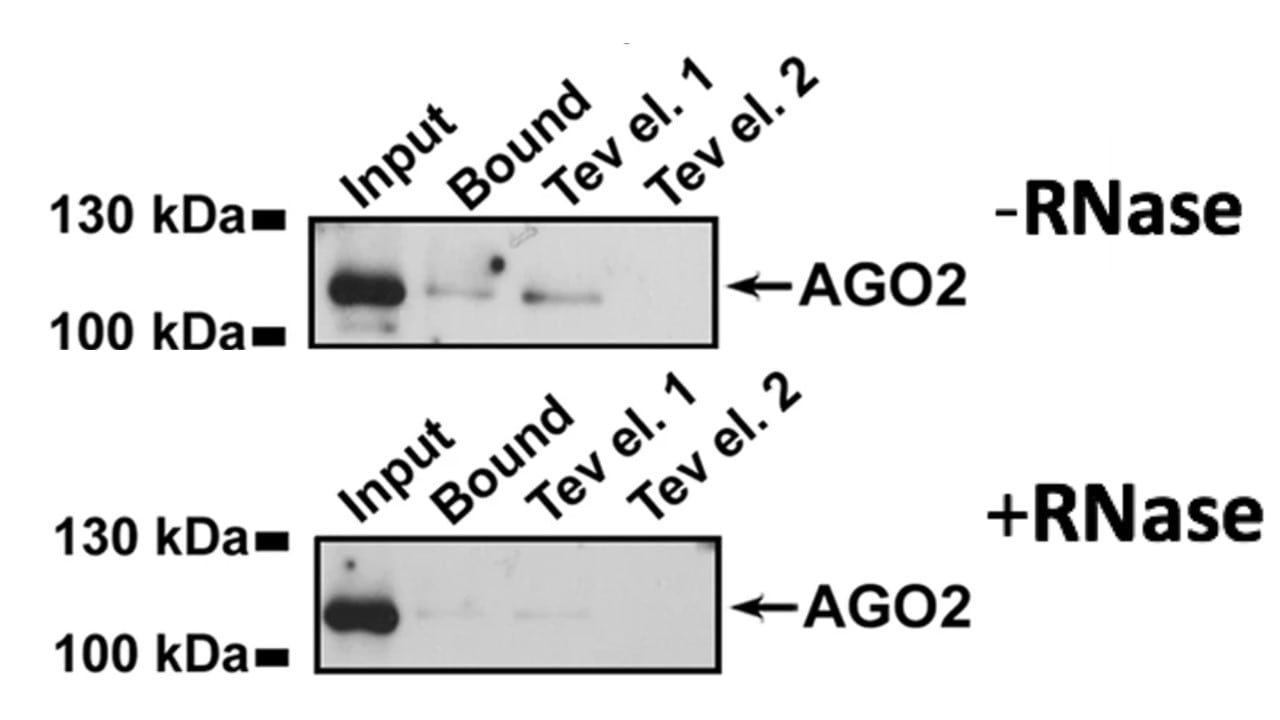
Next, the researchers analyzed ERB2 complex formation with putative binding partner AGO2 in the absence and presence of RNase. The results are shown in Figure 2. The researchers analyzed the nuclear extract (input), the amount of bound AGO2, and two TEV IgG-Sepharose column eluents using a Western blot for AGO2.
Figure 2. Western blot analysis of AGO2 with and without RNase.
1. Which of the following most likely contributes the greatest amount stability to the ERB2-AGO2 interaction?
A) Disulfide bridges
B) Hydrogen bonding
C) Hydrophobic effect
D) Salt bridge
2. Researchers decide to purify ERB2 using a nickel column. They most likely prepare ERB2 with a:
A) C-terminal His6 tag
B) N-terminal Ala6 tag
C) C-terminal Glu8 tag
D) N-terminal Val8 tag
3. To interpret the results of Figure 1, the researchers must assume all of the following EXCEPT:
A) Equal concentrations of RNase were used in the RNase + lanes.
B) Equal concentrations of nuclear extract were loaded in all of the lanes.
C) Equal amounts of ERB in complex with other proteins form in all of the lanes after RNase treatment.
D) The antibody for ERB is specific to the protein at a site distinct from protein interaction sites.
4. Why do researchers include the input lanes in both RNase conditions in Figure 2?
A) To determine the concentration of AGO2 before the experiment
B) To ensure that equal amounts of AGO2 were present before the experimental treatment
C) To measure the amount of ERB2 complex without RNase
D) To increase the likelihood of binding events for later conditions
5. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by Figure 2?
A) An RNA molecule plays a role in the AGO2-ERB2 interaction
B) ERB2 is not expressed when RNase is present
C) AGO2 binds ERB2 more tightly in the absence of RNA
D) AGO2 is upregulated when RNase is present
Answer key for practice passage #1
1. The correct answer is C. The hydrophobic effect provides the most energy stabilization for interactions between proteins (choice C is correct). Disulfide and salt bridges are formed within a protein and not between two different proteins (choices A and D are incorrect). Hydrogen bonding contributes weakly, if at all (choice B is incorrect).
Review hydrophobic effect and thermodynamics.
2. The correct answer is A. His6 tags are added to proteins (at either the N- or C-terminus) to allow the tagged proteins to bind to columns (choice A is correct). The other tags are generally not used in experiments, and they would not be used for a nickel column as His-tags are standard.
Review protein purification techniques and different types of purification columns (i.e. cation-anion exchange, size exclusion, nickel, etc.)
3. The correct answer is C. The western blot provides information on whether or not the ERB2 protein is bound to another protein. When ERB2 runs higher, that means it is bound to another protein as it migrates more slowly through the gel. When ERB2 runs lower, that means it is unbound. Since the ERB2 is seen at different levels in the gel, the researchers cannot assume that equal amounts of ERB2 are in the complex after treatment (choice C is correct). Equal RNase should be used as a control (choice A is incorrect). Equal nuclear extract should be used as a control (choice B is incorrect). In order for the ERB2 antibody to work, it must be able to bind the protein, and it cannot bind if another protein is in the way (choice D is incorrect).
Review Western blotting technique and use of antibodies in molecular biology.
4. The correct answer is B. This lane is a control to ensure that later treatments are not the result of starting with different amounts of material. Since AGO2 is being measured here (as indicated in the figure caption), choice B is correct. Western blots do not provide information about the concentration of protein (choice A is incorrect). AGO2 is being targeted, not ERB2 (choice C is incorrect). Measuring the control will not increase the likelihood for binding events at later experimental stages (choice D is incorrect).
Review Western blotting technique.
5. The correct answer is A. From Figure 2, it is observed that the amount of AGO2 bound to ERB2 decreases after RNase treatment. Therefore, it is reasonable to conclude that an RNA molecule is involved in the AGO2-ERB2 interaction (choice A is correct; choice C is incorrect). ERB2 is not being measured in the Western blot presented in Figure 2 (choice B is incorrect). The input level of AGO2 is the same with or without the RNase, so AGO2 is not upregulated when RNase is present (choice D is incorrect).
Review Western blotting technique.
Gain instant access to the most digestible and comprehensive MCAT content resources available. 60+ guides covering every content area. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.
----
MCAT Biochemistry Practice Passage #2
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a multi-functional organelle and plays a crucial role in protein folding and lipid biosynthesis. Proteins synthesized in the ER are post-translationally modified via N- and O-glycosylation. The sec59 gene encodes a dolichol kinase that is required for N-glycosylation in the ER. Researchers interested in studying the role of sec59 created and characterized a sec59-1 deficient cell line.
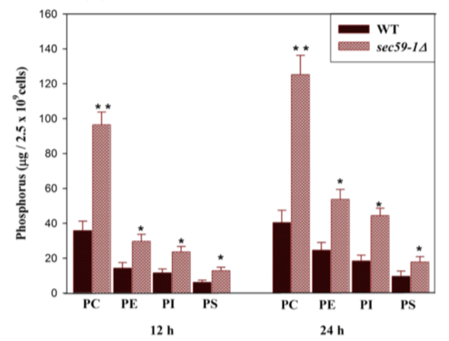
In Experiment 1, researchers created a deletion in sec59-1 and analyzed levels of phosphatidyl choline (PC), phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE), phosphatidyl inositol (PI), and phosphatidyl serine (PS). Equal amounts of WT and sec59-1∆ cells were grown in YPD medium at 30 °C. Equal amounts of cells were harvested in a time-dependent manner, lipids were extracted, phospholipids were separated by two-dimensional TLC, and the amount of phosphorus was quantified. The results are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Relative amounts of various phospholipids in WT versus sec59-1∆ cells.
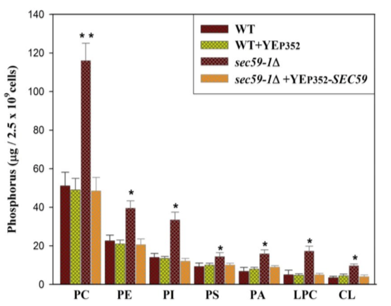
The researchers then hypothesized that an overexpression of sec59 might also have an effect on lipid composition within the ER. To overexpress sec59, researchers cloned the gene into a YEP352 vector. In Experiment 2, the researchers also investigated phosphatidic acid (PA), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and cardiolipin (CL) levels. Researchers investigated WT cells, cells with an overexpression of sec59 through the addition of the YEP352 vector, sec59-1∆ cells, and sec59-1∆ cells rescued by YEP352 vector exogenous sec59-1. The results of this study are shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Relative amounts of various phospholipids with overexpression and deletion of sec59-1.
In Experiment 3, researchers determined that dolichol kinase dependent protein glycosylation directly or indirectly plays a role in suppressing β-oxidation.
CREATOR AND ATTRIBUTION PARTY: JAMES, A., RAVI, C., SRINIVASAN, M., ET AL. CROSSTALK BETWEEN PROTEIN N-GLYCOSYLATION AND LIPID METABOLISM IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. SCI REPORTS 9, 14485 (2019). THE ARTICLE’S FULL TEXT IS AVAILABLE HERE: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-51054-7. THE ARTICLE IS NOT COPYRIGHTED BY SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING. DISCLAIMER: SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING DOES NOT OWN THE PASSAGE PRESENTED HERE. CREATIVE COMMON LICENSE: HTTP://CREATIVECOMMONS.ORG/LICENSES/BY/4.0/. CHANGES WERE MADE TO ORIGINAL ARTICLE TO CREATE AN MCAT-STYLE PASSAGE.
1. Which of the following is the most reasonable conclusion based on Figure 3?
A) WT cells lack adequate levels of ER phospholipids.
B) Cells lacking sec59-1 contain higher levels of phospholipids compared to WT.
C) Sec59-1 acts as a transcription factor to repress phospholipid expression.
D) Sec59-1 is the primary repressor of phospholipid overproduction.
2. According to the results from Figure 4, what effect does sec59-1 overexpression have on phospholipid levels?
A) Increase in phospholipid levels
B) Decrease in phospholipid levels
C) Phospholipid levels remain constant
D) Phospholipids are shunted into gluconeogenesis
A) 28P
B) 30P
C) 28Al
D) 30Al
4. Researchers observe an increase in acetyl-CoA in sec59-1∆ cells. Based on information from the passage, which of the following explanations best describes this observation?
A) Sec59-1 deficient cells produce higher levels of phospholipids, which are converted into acetyl-CoA through β-oxidation.
B) Sec59-1 deficient cells must decrease flux through glycolysis in order to conserve energy.
C) Acetyl-CoA accumulates as the Krebs Cycle stops.
D) Cells with Sec59-1 can only use phospholipids for energy production, causing β-oxidation to occur more rapidly.
5. The YEP352 plasmid encodes a gene for ampicillin resistance. Researchers treating a YEP352-transformed bacterial colony with ampicillin should expect:
A) Surviving cells to have lower levels of PC when compared to PC levels in untransformed cells.
B) Surviving cells to have similar levels of PE and PI when compared to PE and PI levels in untransformed cells.
C) Some YEP352 cells remain sensitive to ampicillin.
D) Acquired resistance to develop rapidly in cells with the YEP352 plasmid.
Answer key for practice passage #2
1. The correct answer is B. Based on the results from Figure 3, we see that the levels of various phospholipids increase in the sec59-1 knockout. We can therefore conclude that cells lacking sec59-1 contain higher levels of phospholipids compared to WT without making any other assumptions outside of the data itself (choice B is correct). WT levels of phospholipids are adequate as they are wild-type, or normal, levels (choice A is incorrect). Sec59-1 is a kinase, not a transcription factor, and the passage does not provide any indication that the protein may act as a transcription factor (choice C is incorrect). While losing sec59-1 does lead to increased phospholipid levels, it is too extreme to state that sec59-1 is the primary repressor of phospholipid production (choice D is incorrect).
Practice interpreting experimental data, and make sure to understand the figure completely.
2. The correct answer is C. Sec59-1 overexpression is shown by the green bar in the bar graph (contains the YEP352 plasmid vector with the sec59-1 gene inside). The levels are not significantly different from WT (choice C is correct; choices A and B are incorrect). The data from Figure 4 does not support the conclusion in answer choice D.
Reviewing molecular cloning and gene overexpression. Practice interpreting experimental data, and make sure to understand the figure completely.
3. The correct answer is C. An alpha particle is written as 4He, and by losing it, the mass number of 32P decreases from 32 to 28. Then, the atomic number of 15 (not written in normal convention) decreases by 2 to 13, which is the atomic number for aluminum.
Review nomenclature used on the periodic table. Review radioactive decay.
4. The correct answer is A. Figures 3 and 4 demonstrate that sec59-1 deficient cells have higher levels of phospholipids. The passage also states that sec59-1 suppresses β-oxidation. Combining these two pieces of information, it can be concluded that sec59-1 deficient cells produce higher levels of phospholipids, which are converted into acetyl-CoA through β-oxidation (choice A is correct). Energy conservation is not discussed (choice B is incorrect). The Krebs cycle does not stop (choice C is incorrect). Phospholipids are not the only source of energy (carbohydrates can be used) in sec59-1 normal cells (choice D is incorrect).
Review β-oxidation. Review the integration of acetyl-CoA into metabolism.
5. The correct answer is B. Figure 4 demonstrates that overexpression of sec59-1 does not change phospholipid levels in the cells. So, even in the cells that are successfully transformed and selected for, the sec59-1 overexpression will have no effect (choice B is correct; choice A is incorrect). Cells that were successfully transformed with the plasmid will be resistant to ampicillin (choice C is incorrect). The cells with the plasmid are already resistant to ampicillin (choice D is incorrect).
Review molecular cloning and antibiotic selection.
----
MCAT Biochemistry Practice Passage #3
Vibrio anguillarum 531A, which is isolated from a diseased fish in the Atlantic Ocean, is a mixture composed of about 95% and 5% of highly pigmented cells (strain 531Ad) and cells with normal levels of pigmentation (strain 531Ac), respectively. Analysis of the V. anguillarum 531Ad DNA region encompassing genes involved in the tyrosine metabolism showed a 410-bp duplication within the hmgA gene that results in a frameshift and early termination of translation of the homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase. Researchers hypothesized that this mutation results in the accumulation of homogentisate that is oxidized and polymerized to produce pyomelanin.
To investigate the origins of strain531Ad and strain531Ac, researchers cultured them separately. First, they found that a strain531Ad culture had a brown color while a strain531Ac culture was clear. Then, researchers carried out whole-genome sequencing. In both of the cultures, researchers found 23 different mutations, including the hmgA mutation. They also identified a Q349P mutation in the tyrosine-specific transport protein (TyrP) coding sequence. Software folding simulations did not show structural changes in the protein, leading researchers to believe that the amino acid change does not affect tyrosine uptake.
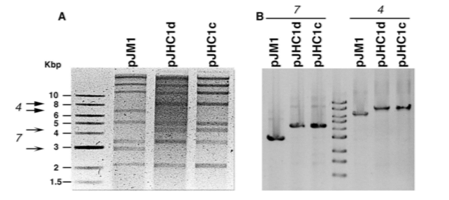
Next, researchers wanted to ensure that strains 531Ad and 531Ac derived from one another. V. anguillarum harbors a pJM1-type plasmid of which most strains slightly differ, and endonuclease digestion was carried out to determine whether or not restriction patterns between 531Ad and 531Ac were identical.
Figure 5. Restriction digestion patterns of 531Ad (pJHC1d) and 531Ac (pJHC1c).
In a final study, researchers complemented strain 531Ad with a recombinant clone harboring hmgA. This restored the original color to the colonies, confirming that in the absence of homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, homogentisate accumulates and undergoes nonenzymatic oxidation and polymerization resulting in high amounts of the brown pigment.
CREATOR AND ATTRIBUTION PARTY: BATALLONES, V., FERNANDEZ, J., FARTHING, B., ET AL. DISRUPTION OF HMGA BY DNA DUPLICATION IS RESPONSIBLE FOR HYPERPIGMENTATION IN A VIBRIO ANGUILLARUM STRAIN. SCI REPORTS 9, 14589 (2019). THE ARTICLE’S FULL TEXT IS AVAILABLE HERE: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-51126-8. THE ARTICLE IS NOT COPYRIGHTED BY SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING. DISCLAIMER: SHEMMASSIAN ACADEMIC CONSULTING DOES NOT OWN THE PASSAGE PRESENTED HERE. CREATIVE COMMON LICENSE: HTTP://CREATIVECOMMONS.ORG/LICENSES/BY/4.0/. CHANGES WERE MADE TO ORIGINAL ARTICLE TO CREATE AN MCAT-STYLE PASSAGE.
1. Based on Figure 5, which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?
A) The strains come from different genetic origins.
B) The two strains are derived from a common origin.
C) The 531Ac strain was taken up via transformation.
D) Early V. anguillarum produced strain 531Ad first, which then mutated into strain 531Ac.
2. Researchers add exogenous homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase mRNA to a culture of strain 531Ad. Which of the following is the most likely result?
A) The brown pigment remains.
B) The clear pigment remains.
C) The brown pigment turns into a clear pigment over time.
D) The clear pigment turns into a brown pigment over time.
3. A student identifies an active site mutation in the hmgA protein leading to its inactivation. Which of the following is the most likely mutation?
A) A77V
B) E77D
C) Q77N
D) R77Q
4. The information in the passage suggests that which of the following molecules produces the brown pigment?
A) 531Ad
B) 531Ac
C) Pyomelanin
D) Homogentisate
5. Which of the following best describes the Michaelis-Menten plot of hmgA if it shows cooperativity?
A) Hyperbolic
B) Quadratic
C) Sigmoidal
D) Exponential
Answer key for practice passage #3
1. The correct answer is B. The passage indicates that most strains of the pJM1 plasmid slightly differ in sequence. If two plasmids have the same sequence, it is likely that they are derived from the same origin. In a restriction digestion experiment, plasmids have the same sequence if the banding patterns after digestion are the same. Figure 6 shows that the banding patterns for pJHC1d and pJHC1c are identical (choice B is correct; choice A is incorrect). Figure 6 provides no evidence for how the plasmids were taken up or the order by which they were taken up (choices C and D are incorrect).
Review endonucleases and restriction digestion. Practice interpreting experimental data, and make sure to understand the figure completely.
2. The correct answer is A. The passage states that homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase translation is disrupted, meaning functional versions of the protein are not produced. This ultimately causes brown pigmentation. If exogenous mRNA for the protein was added, however, that would not fix the problem as the passage indicates that it is a problem with translation, not transcription. Therefore, an accumulation of homogentisate would still occur and eventually lead to the brown color after oxidation and polymerization (choice A is correct).
Review transcription versus translation.
3. The correct answer is D. A mutation from a positively charged species to a polar uncharged species in the active site is the most likely to inactivate a protein when compared to the other choices (choice D is correct). The A77V mutation maintains a hydrophobic and aliphatic amino acid (choice A is incorrect). The E77D mutation maintains a negatively charged amino acid (choice B is incorrect). The Q77N maintains a polar uncharged amino acid (choice C is incorrect).
Review amino acids.
4. The correct answer is C. The passage indicates that the accumulation of homogentisate is oxidized and polymerized to produce pyomelanin. The passage also states that “homogentisate accumulates and undergoes nonenzymatic oxidation and polymerization resulting in high amounts of the brown pigment.” Through these similar statements, we see that pyomelanin is the brown pigment (choice C is correct). 531Ad and 531Ac are not molecules, but they are entire cells (choices A and B are incorrect). Homogentisate is the precursor to pyomelanin, but it itself does not produce brown pigment (choice D is incorrect).
Read through the passage again—this question is similar to a CARS question.
5. The correct answer is C. The Michaelis-Menten plot for a cooperative enzyme displays a sigmoidal curve (choice C is correct). In general, cooperativity shows sigmoidal curves for all types of plots.
Review enzymes, Michaelis-Menten plots, and cooperativity.
Want more MCAT Practice Questions? Check out our proprietary MCAT Question Bank for 4000+ sample questions and eight practice tests covering every MCAT category.
Gain instant access to 4,000+ representative MCAT questions across all four sections to identify your weaknesses, bolster your strengths, and maximize your score. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.
----
MCAT Biochemistry Practice Questions (Standalone)
1. Which of the following mutations to solvent-exposed residues in a protein is likely to have the greatest entropic penalty?
A) A76V
B) E99D
C) R287A
D) Y78P
2. Researchers mutate a codon at the third nucleotide position, resulting in a silent mutation. Which principle best describes this phenomenon?
A) Canonical Watson-Crick base pairing
B) Wobble base pair
C) mRNA flexibility
D) Posttranscriptional modifications
3. Researchers are testing the kinetics of a novel enzyme inhibitor. After assessing Michaelis-Menten kinetics, they conclude that the inhibitor binds to both the enzyme alone and the enzyme-substrate complex, though it binds to the enzyme alone with a slightly higher affinity. This is an example of:
A) Competitive inhibition
B) Noncompetitive inhibition
C) Uncompetitive inhibition
D) Mixed inhibition
4. A DNA-binding protein is found to contain several arginine residues in the DNA-binding pocket. Which region of DNA does this protein most likely interact with?
A) Nitrogenous base
B) 2’ H
C) 3’ OH
D) Phosphate backbone
5. A student sets up a size-exclusion column to separate a reaction mixture containing a small dye, a large protein, and a protein-dye complex. Which of the following is the MOST likely to elute first from the column?
A) Dye alone
B) Dye-dye dimer
C) Protein
D) Protein-dye
Answer key for standalone practice questions
1. Answer choice C is correct. Answer choices A and D are incorrect as the mutations maintain an entropic penalty but do not introduce a new one. Answer choice B is incorrect as the mutation maintains a favorable solvent-exposed residue as both E and D are negatively charged. Answer choice C is correct because the mutation of a positively charged arginine to a hydrophobic alanine would increase the need for ordered water molecules, thereby introducing an entropic penalty.
2. Answer choice B is correct. The wobble base pair explains why multiple codons may encode the same amino acid. A silent mutation occurs when the same amino acid is produced after the mutation, and the wobble base pair theory best explains this (choice B is correct). Canonical Watson-Crick base pairing describes A-T or G-C base pairs, but the third position in a codon often employs non-canonical base pairing (choice A is incorrect). mRNA flexibility is not involved in the processes described in the question stem (choice C is incorrect). Posttranslational modifications occur on proteins and are not involved in the processes described in the question stem (choice D is incorrect).
3. Answer choice D is correct. Mixed inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds both the enzyme alone and the enzyme-substrate complex. In this case, the inhibitor may bind the enzyme alone 60% of the time while binding the enzyme-substrate complex 40% of the time. Competitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds the active site of an enzyme (choice A is incorrect). Noncompetitive inhibition is a subclass of mixed inhibition that describes an inhibitor binding an allosteric site, and this type of inhibitor binds the enzyme alone and enzyme-substrate complex with equal affinity (choice B is incorrect). Uncompetitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds the enzyme-substrate complex alone (choice C is incorrect).
4. Answer choice D is correct. The phosphate backbone is negatively charged, so it can interact with the positively charged arginine residues. The nitrogenous base (A, T, C, G) is less likely to form a strong interaction with the positively charged residues (choice A is incorrect). The 2’ H and 3’ OH are small and will interact very weakly with the arginine residues (choices B and C are incorrect).
5. Answer choice D is correct. The largest molecules elute first from a size-exclusion column because the smaller molecules fall into pores that require a longer path. The dye alone, dye-dye dimer, and protein are much smaller and will therefore take a longer time to pass through the column (choices A-C are incorrect).